



Quick Links:
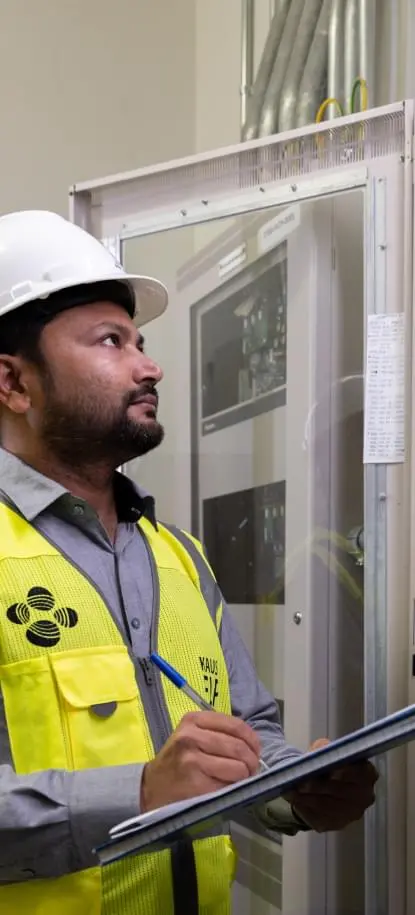



To prevent electrical hazards, always make sure equipment is properly grounded. Electrical grounding provides an alternate path for electricity to follow, rather than going through a person.
Equipment with a grounding prong must be plugged into an extension cord with a ground. the grounding plug should not be removed from the equipment.
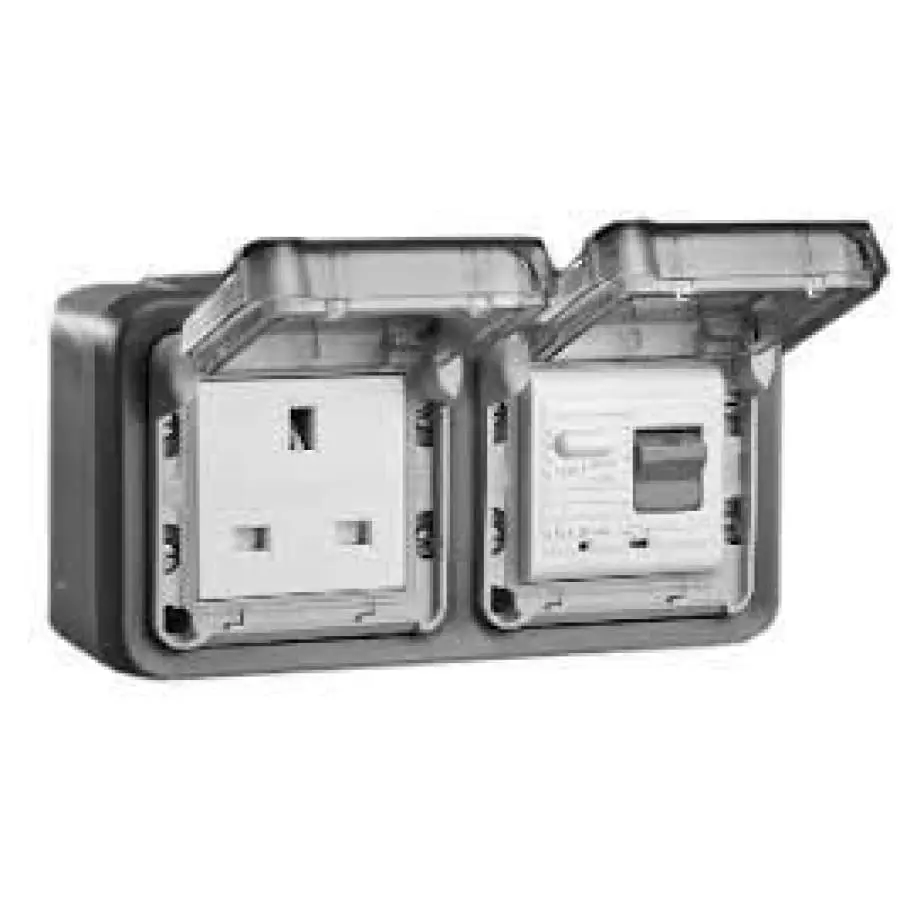
When using electricity in a wet or damp location, including outdoor locations, a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) must be used. The GFCI ensures that any electrical shock is brief.
Although painful, it wouldn’t be fatal because the GFCI creates a ground fault or leak in the current.
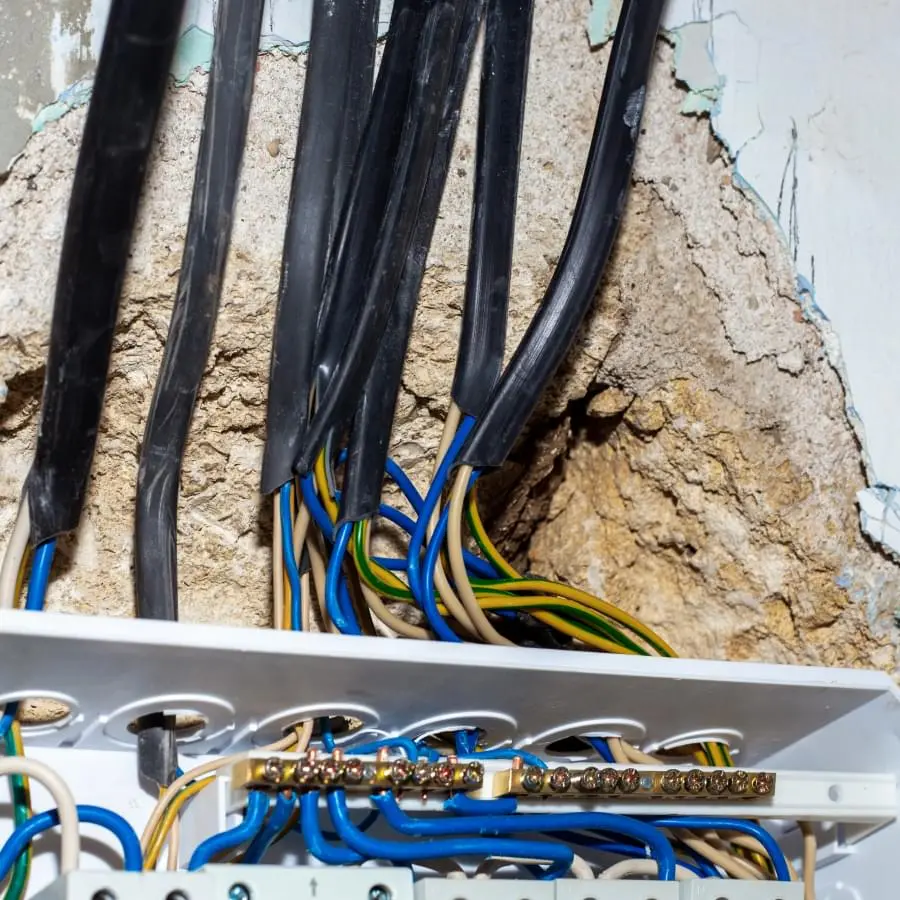


When servicing and maintenance tasks involve electricity and electrical equipment, you must prevent the unexpected startup of equipment. More information on lockout/tagout procedures is available on the SOP Isolation, Lockout & use of hold tags process.
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters protect users of electrically-powered tools and equipment from electrical shocks, especially when working in wet environments. The following are situations when a GFCI is required for electrically-powered equipment and tools:

The GFCI can be located on the extension cord, outlet, or the circuit breaker. A GFCI is required in outlets that are installed around sinks or any other areas where water may present. GFCIs must be UL-approved and used within the manufacturer’s guidelines.