



Quick Links:



KAUST Non-Ionizing Radiation (NIR) Safety program has been developed to protect the research community and the general public and environment, from devices and equipment that produces potentially hazardous levels of NIR, and also to facilitate and ensure the safe use/work around these equipment in KAUST laboratories and classrooms, and to assist with compliance to applicable standards, guidelines and international best practices.
Moustafa El-Soubki




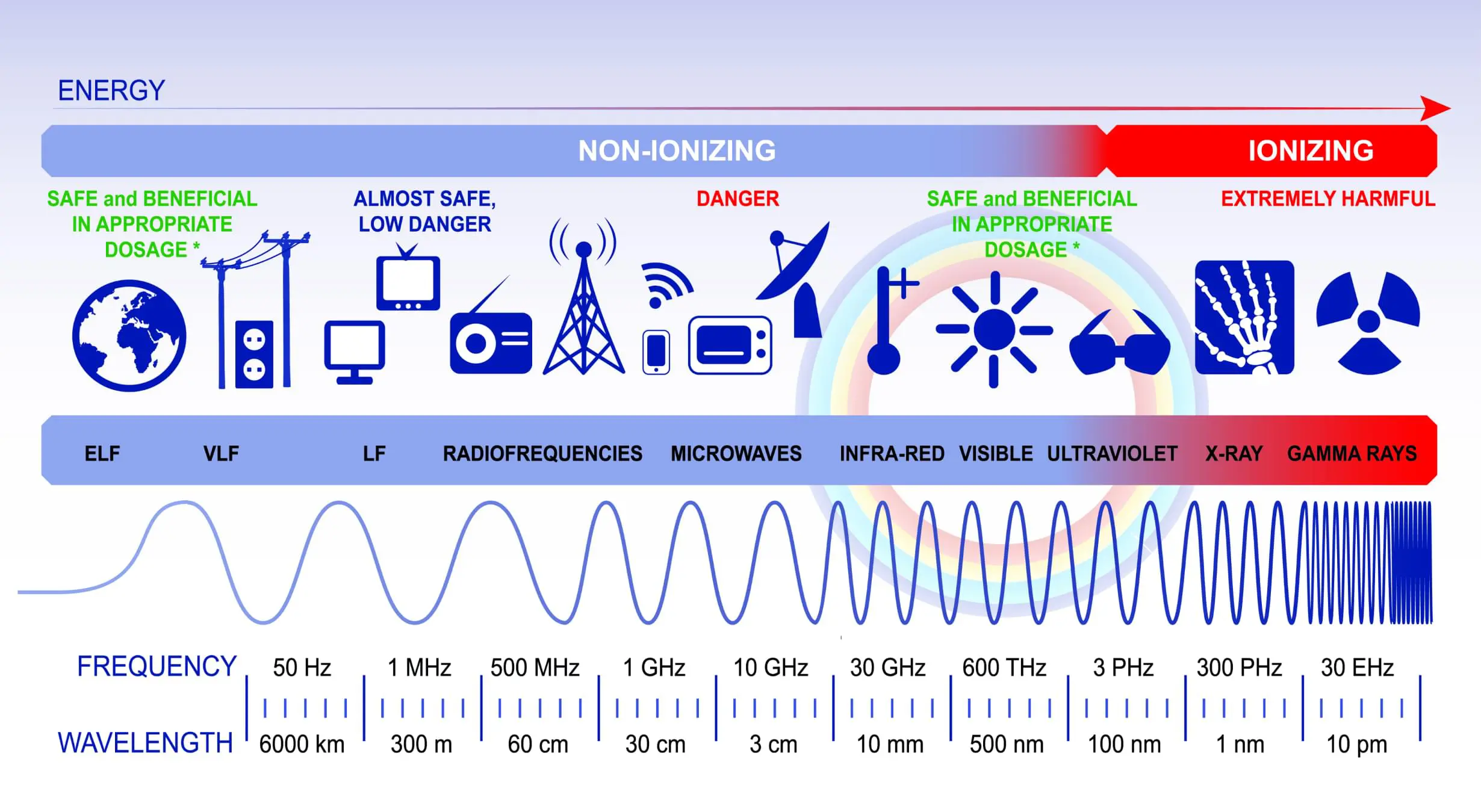
The modern world is full of devices which, either directly or indirectly, act as sources of non-ionizing radiation. Non-ionizing radiation refers to electromagnetic radiations that have wavelengths/frequencies ranging from 100 nm to static fields. This type of electromagnetic radiation does not have sufficient energy to ionize (remove electrons from) atoms or molecules; instead the energy is converted to heat. In general, non-ionizing radiation tends to be less hazardous to humans than ionizing radiation (ionizing radiation has a wavelength less than 100 nm or a photon energy greater than 12.4 electron volts). However, depending on the wavelength/frequency, the exposure time and the irradiance (or power density) values, non-ionizing radiation sources may present a human health hazard. Therefore, those working with non-ionizing radiation sources must take precautions to ensure they are not exposed to excessive levels.
The sources of non-ionizing radiation within the University are varied and include ultraviolet lamps, microwave ovens, and high intensity magnets including nuclear magnetic resonance, induction heaters, transmission generators, Wi-Fi, mobile phones, cell antennas and more.
For more information, please refer to the sections below which provide safety guidelines to help maintain a safe working environment when using sources of non-ionizing radiation.
Laboratories using ultraviolet (UV) equipment should review the following documents:
Devices or sources which are protected by safety interlock (i.e. exposure to UV under normal operating condition is impossible) need only a few precautions such as warning signs and UV Safety Training though the HSE LMS portal.
Devices or sources where exposure to UV is possible, or even inevitable, require a risk assessment which will enable to determine if additional control measures are required.


Laboratory using equipment emitting radiofrequency or microwave radiation should review the Radiofrequency and Microwave Safety Awareness document. Users of microwave oven are encouraged to take the Microwave Safety Training.
Microwave are high frequency radio waves; they are primarily used for TV broadcasting, radar or air and sea navigational aids, telecommunication including mobile phones as well as in many kitchens for cooking.
Microwaves are reflected, transmitted or absorbed by materials in their path, in a similar manner to visible light. Metallic materials totally reflect microwaves while non-metallic materials such as glass and some plastics are mostly transparent to microwaves. Materials containing water, for example foods, fluids or tissues, readily absorb microwave energy, which is then converted into heat. More details about microwave ovens safety fields are available in WHO Fact Sheets 182.
In research laboratories, microwave ovens are often used to warm or sterilize. Leakage survey of microwave ovens is not carried out by the Health, Safety and Environment Team; indeed microwave ovens that have intact doors and door seals should not produce excessive microwave leakage.
Any unit that is considered irreparable must be rendered inoperable by removing the plug and cord before disposal.

Laboratory using strong permanent magnets, electromagnets as well as superconducting magnets should review the following documents:
The Principal Investigator (PI) or Center Director must ensure that the personnel , or authorized users, are adequately trained before allowing/authorizing them to operate, maintain, service or work in the vicinity or with devices that contains or emits NIR. The following online training material are available on the HSE LMS portal:
