


Quick Links:
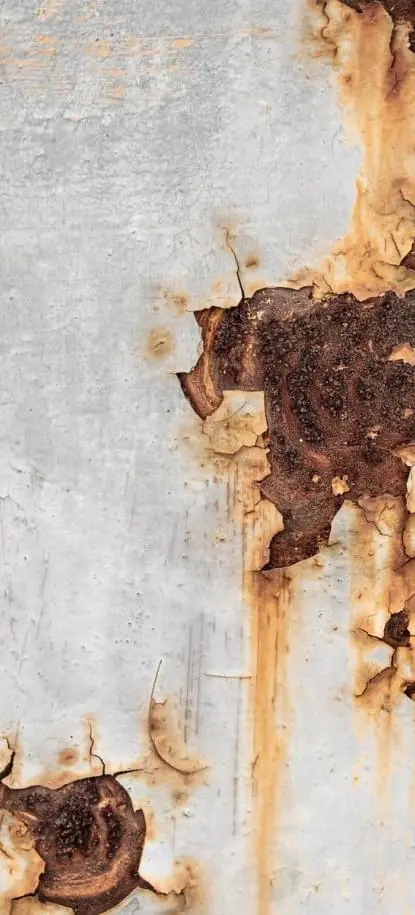


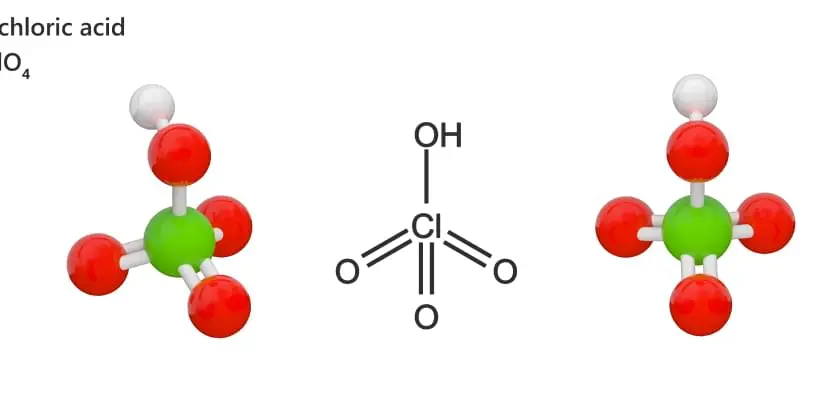
Corrosive materials not only damage human tissue but also corrode metals and some other materials and can be further classified into either acidic or basic (caustic or alkali) materials. Acidic corrosives have a low pH (pH 0-5) whereas basic corrosives have a high pH (pH 11-14). Note: pH values are on a logarithmic scale and not linear. More so than other hazard class, corrosive materials chemically and readily react with many other materials. This reactivity adds another dimension to the hazard profile of corrosive materials, for they can react (aka chemical incompatibilities) to create other hazards in the form of explosive and toxic materials as well as generate heat and pressures.
This reactivity explains why corrosive materials are a ubiquitous and widely used hazard class in many settings (home use, kitchens, etc) and not just laboratories. Their functionality and usefulness dictates it. This ubiquitous and widely used status of corrosive materials helps explain the concern of why many people need to be aware of its destructive and hazardous nature and the precautions necessary to protect oneʼs health and safety but also of their equipment as well.
Watch the videos below showing the corrosive effect of acids and bases on materials as well as an overview of corrosive material injuries.
To help address these safety concerns the Research Safety Team has created the below safety resources for KAUST personnel to use to understand the safety aspects of dealing with Corrosive Materials.